Azure - Exam
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing?
Imagine you have a big box full of great books and you want to share them with your friends who live far away. But instead of giving them the books directly, you decide to put all the books in a special storage at a location. Now, your friends can come to that special storage whenever they want and read with the books without having to take them home. So they don't buy the books, but just pay a nominal rent or fees for reading the books. That special storage is your cloud computing and the rent/fees they pay is pay-as-you-go pricing model.
Wired example 😀, I know but I hope it will help you easily visualize Cloud Computing.
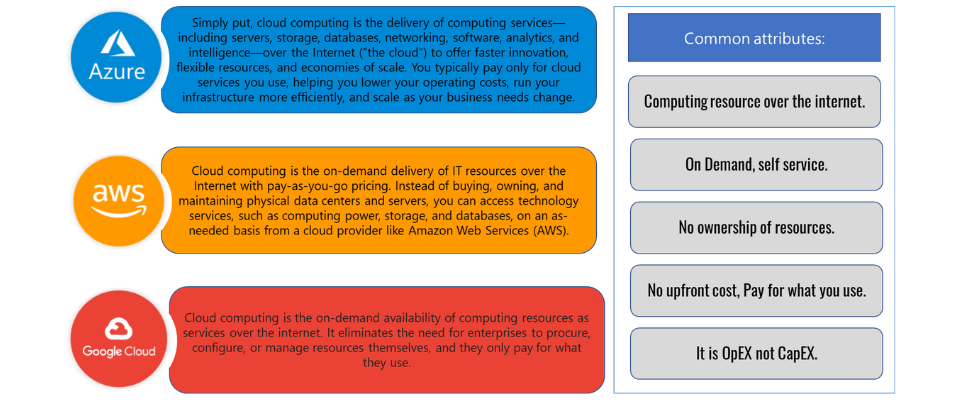
So, Cloud technologies refer to a collection of computing resources, services, and infrastructure that are delivered over the internet ("the cloud") by cloud service providers. Instead of relying solely on on-premise data centers, organizations can leverage the power and flexibility of the cloud to meet their computing needs.
Service Models
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) is a type of cloud computing service that offers essential compute, storage, and networking resources on demand, on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Platform as a service refers to cloud computing services that supply an on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering, and managing software applications.
Software as a service is a method for delivering software applications over the internet, on demand, and typically on a subscription basis. With SaaS, cloud providers host and manage the software application and underlying infrastructure.
Deployment Models
- Public cloud
- Private cloud
- Hybrid cloud
A cloud computing model in which a third-party provider makes computing resources available to the general public over the internet. With the public cloud, companies do not have to set up and maintain their own data centers.
A cloud computing model in which a company uses a proprietary architecture and runs cloud servers within its own data center.
A cloud computing model that includes a mix of on-premises, private cloud and third-party public cloud services.
Use cases of Cloud Computing | Where to use Cloud Computing?
- Storing and accessing files:
- Using software and apps:
- Sharing and collaborating:
- Powerful computing:
You can save your pictures, videos, and documents in the cloud, so you can access them from any device with an internet connection. It's like having your stuff available wherever you go, without carrying it all with you.
Instead of installing programs directly on your computer, you can use software and apps that are located in the cloud. For example, you can use online tools for drawing, writing, or playing games without needing to download anything.
With cloud computing, it's easy to share files and work together with others on projects. You can invite your friends or classmates to edit a document or work on a presentation together, even if they are in different places.
The computers in the cloud are very powerful, so they can handle complex tasks and calculations. You can use them to analyze big amounts of data, run simulations, or even train artificial intelligence models.
Benefits Cloud Computing.
- Cost:
- Agility:
- Secure:
- Global Scale:
Switching to the cloud can save companies a ton of money on their IT expenses. See, cloud computing gets rid of all those upfront costs of buying hardware, software, and running datacenters on-site. You know, those rows of servers, the never-ending electricity bills for power and cooling, and the tech whizzes needed to manage everything. It all adds up real quick, and cloud computing takes that burden off your wallet.
The cloud offers you a bunch of cool tech tools to play with, making it super easy to come up with innovative ideas and create almost anything you can dream up. Need some extra computing power, storage space, or databases? No problem! You can get them up and running in a snap. From fancy stuff like Internet of Things and machine learning to data lakes and analytics, the cloud's got you covered. And the best part? You can deploy all these tech services in just a few minutes! It's like magic – you can turn your ideas into reality way faster than ever before. This speedy process lets you be creative and try out new stuff to give your customers the best experience possible. Plus, it's a game-changer for transforming your business and staying ahead of the competition. So go ahead, unleash your imagination, and let the cloud power up your wildest ideas!
When companies wonder about the security risks of cloud computing, the good news is that they're actually quite low. The security in cloud computing is usually way better than what you'd find in typical company data centers. Why? 'Cause cloud providers go all out with their security measures, making them super safe. These cloud folks really know their stuff and have top-notch security teams that are considered the best in the business. So, when it comes to keeping your data safe and sound, you can trust the cloud to have your back!
Using the cloud lets you go big and global in no time! Azure, AWS and GCP for example; they've got servers all around the globe. So, with just a few clicks, you can spread your application to multiple places. This way, your users get faster access, and their experience gets way better. One of the cool things about cloud computing is its elastic scaling. Sounds fancy, right? Well, it just means you can easily adjust the amount of IT resources you need. Whether it's more computing power, storage, or bandwidth, the cloud's got you covered. And it all happens exactly when and where you need it. So, no more stressing about having too much or too little – the cloud's got that balance just right!